
Facebook and Google were far from the only developers openly abusing Apple’s Enterprise Certificate program meant for companies offering employee-only apps. A TechCrunch investigation uncovered a dozen hardcore pornography apps and a dozen real-money gambling apps that escaped Apple’s oversight. The developers passed Apple’s weak Enterprise Certificate screening process or piggybacked on a legitimate approval, allowing them to sidestep the App Store and Cupertino’s traditional safeguards designed to keep iOS family friendly. Without proper oversight, they were able to operate these vice apps that blatantly flaunt Apple’s content policies.
The situation shows further evidence that Apple has been neglecting its responsibility to police the Enterprise Certificate program, leading to its exploitation to circumvent App Store rules and forbidden categories. For a company whose CEO Tim Cook frequently criticizes its competitors for data misuse and policy fiascos like Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica, Apple’s failure to catch and block these porn and gambling demonstrates it has work to do itself.
Porn apps PPAV and iPorn (iP) continue to abuse Apple’s Enterprise Certificate program to sidestep the App Store’s ban on pornography. Nudity censored by TechCrunch
TechCrunch broke the news last week that Facebook and Google had broken the rules of Apple’s Enterprise Certificate program to distribute apps that installed VPNs or demanded root network access to collect all of a user’s traffic and phone activity for competitive intelligence. That led Apple to briefly revoke Facebook and Google’s Certificates, thereby disabling the companies’ legitimate employee-only apps which caused office chaos.
Apple issued a fiery statement that “Facebook has been using their membership to distribute a data-collecting app to consumers, which is a clear breach of their agreement with Apple. Any developer using their enterprise certificates to distribute apps to consumers will have their certificates revoked, which is what we did in this case to protect our users and their data.” Meanwhile, dozens of prohibited apps were available for download from shady developers’ websites.

Apple offers a lookup tool for finding any business’ D-U-N-S number, allowing shady developers to forge their Enterprise Certificate application
The problem starts with Apple’s lax standards for accepting businesses to the enterprise program. The program is for companies to distribute apps only to their employees, and its policy explicitly states “You may not use, distribute or otherwise make Your Internal Use Applications available to Your Customers”. Yet Apple doesn’t adequately enforce these policies.
Developers simply have to fill out an online form and pay $299 to Apple, as detailed in this guide from Calvium. The form merely asks developers to pledge they’re building an Enterprise Certificate app for internal employee-only use, that they have the legal authority to register the business, provide a D-U-N-S business ID number, and have an up to date Mac. You can easily Google a business’ address details and look up their D-U-N-S ID number with a tool Apple provides. After setting up an Apple ID and agreeing to its terms of service, businesses wait one to four weeks for a phone call from Apple asking them to reconfirm they’ll only distribute apps internally and are authorized to represent their business.
With just a few lies on the phone and web plus some Googleable public information, sketchy developers can get approved for an Apple Enterprise Certificate.

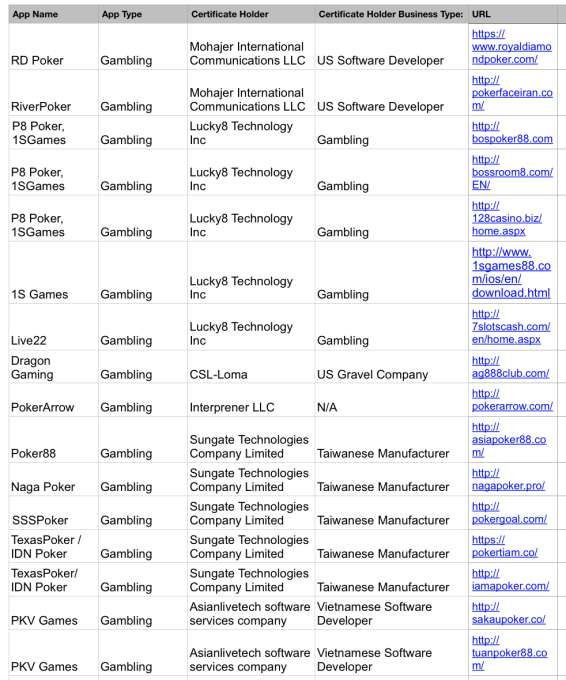
Real-money gambling apps openly advertise that they have iOS versions available that abuse the Enterprise Certificate program
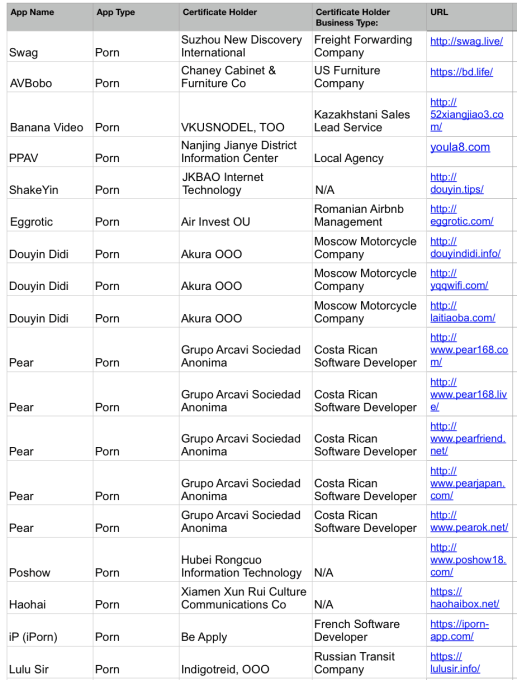
Given the number of policy-violating apps that are being distributed to non-employees using registrations for businesses unrelated to their apps, it’s clear that Apple needs to tighten the oversight on the Enterprise Certificate program. TechCrunch found thousands of sites offering downloads of “sideloaded” Enterprise apps, and investigating just a sample uncovered numerous abuses. Using a standard un-jailbroken iPhone. TechCrunch was able to download and verify 12 pornography and 12 real-money gambling apps over the past week that were abusing Apple’s Enterprise Certificate system to offer apps prohibited from the App Store. These apps either offered streaming or pay-per-view hardcore pornography, or allowed users to deposit, win, and withdraw real money — all of which would be prohibited if the apps were distributed through the App Store.

A whole screen of prohibited sideloaded porn and gambling apps TechCrunch was able to download through the Enterprise Certificate system
In an apparent effort to step up policy enforcement in the wake of TechCrunch’s investigation into Facebook and Google’s Enterprise Certificate violations, Apple appears to have disabled some of these apps in the past few days, but many remain operational. The porn apps that we discovered which are currently functional include Swag, PPAV, Banana Video, iPorn (iP), Pear, Poshow, and AVBobo, while the currently functional gambling apps include RD Poker and RiverPoker.
The Enterprise Certificates for these apps were rarely registered to company names related to their true purpose. The only example was Lucky8 for gambling. Many of the apps used innocuous names like Interprener, Mohajer International Communications, Sungate, and AsianLiveTech. Yet others seemed to have forged or stolen credentials to sign up under the names of completely unrelated but legitimate businesses. Dragon Gaming was registered to US gravel supplier CSL-LOMA. As for porn apps, PPAV’s certificate is assigned to the Nanjing Jianye District Information Center, Douyin Didi was licensed under Moscow motorcycle company Akura OOO, Chinese app Pear is registered to Grupo Arcavi Sociedad Anonima in Costa Rica, and AVBobo covers its tracks with the name of a Fresno-based company called Chaney Cabinet & Furniture Co.
You can see a full list of the policy violating apps we found below:
Apple refused to explain how these apps slipped into the Enterprise Certificate app program. It declined say if it does any follow-up compliance audits on developers in the program or if it plans to change admission process. An Apple spokesperson did provide this statement, though, indicating it will work to shut these apps down and potentially ban the developers from building iOS products entirely:
“Developers that abuse our enterprise certificates are in violation of the Apple Developer Enterprise Program Agreement and will have their certificates terminated, and if appropriate, they will be removed from our Developer Program completely. We are continuously evaluating the cases of misuse and are prepared to take immediate action.”
TechCrunch asked Guardian Mobile Firewall’s security expert Will Strafach to look at the apps we found and their Certificates. Strafach’s initial analysis of the apps didn’t find any glaring evidence that the apps misappropriate data, but they all do violate Apple’s Certificate policies and provide content banned from the App Store. “At the moment, I have noticed that action is slower regarding apps available from an independent website and not these easy-to-scrape app directories” that occasionally crop up offering centralized access to a plethora of sideloaded apps.
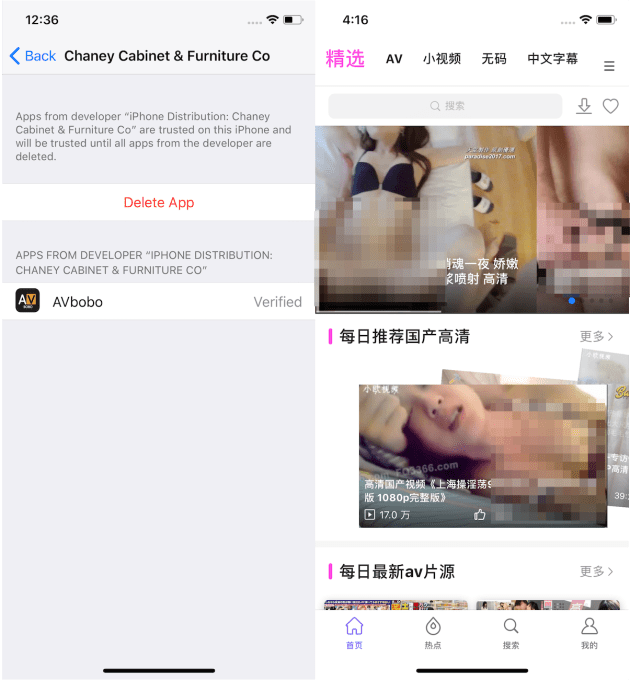
Porn app AVBobo uses an Enterprise Certificate registered to Fresno’s Chaney Cabinet & Furniture Co
Strafach explained how “A significant number of the Enterprise Certificates used to sign publicly available apps are referred to informally as ‘rogue certificates’ as they are often not associated with the named company. There are no hard facts to confirm the manner in which these certificates originate, but the result of the initial step is that individuals will gain control of an Enterprise Certificate attributable to a corporation, usually China/HK-based. Code services are then sold quietly on Chinese language marketplaces, resulting in sometimes 5 to 10 (or more) distinct apps being signed with the same Enterprise Certificate.” We found Sungate and Mohajer Certificates were farmed out for use by multiple apps in this way.
“In my experience, Enterprise Certificate signed apps available on independent websites have not been harmful to users in a malicious sense, only in the sense that they have broken the rules” Strafach notes. “Enterprise Certificate signed apps from these Chinese ‘helper’ tools, however, have been a mixed bag. Zoe example, in multiple cases, we have noticed such apps with additional tracking and adware code injected into the original now-repackaged app being offered.”

Porn apps like Swag openly advertise their availability on iOS
Interestingly, none of the off-limits apps we discovered asked users to install a VPN like Google Screenwise, let alone root network access like Facebook Research. TechCrunch reported this month that both apps had been paying users to snoop on their private data. But the iOS versions were banned by Apple after we exposed their policy violations, and Apple also caused chaos at Facebook and Google’s offices by temporarily shutting down their employee-only iOS apps too. The fact that these two US tech giants were more aggressive about collecting user data than shady Chinese porn and gambling apps is telling.“This is a cat-and-mouse game” Strafach concluded regarding Apple’s struggle to keep out these apps. But given the rampant abuse, it seems Apple could easily add stronger verification processes and more check-ups to the Enterprise Certificate program. Developers should have to do more to prove their apps’ connection with the Certificate holder, and Apple should regularly audit certificates to see what kind of apps they’re powering.
Back when Facebook missed Cambridge Analytica’s abuse of its app platform, Cook was asked what he’d do in Mark Zuckerberg’s shoes. “I wouldn’t be in this situation” Cook frankly replied. But if Apple can’t keep porn and casinos off iOS, perhaps Cook shouldn’t be lecturing anyone else.
Be the first to comment